Understanding Melanoma: The Skin Cancer You Shouldn’t Ignore

When it comes to skin health, there’s one word that often rings alarm bells: melanoma. Known as the most dangerous form of skin cancer, melanoma doesn’t just stay on the surface—it can spread rapidly and become life-threatening if not caught early. But with the right knowledge and a proactive approach, melanoma is often treatable. Here’s what you need to know.
What Is Melanoma?
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer that starts in the melanocytes—the cells that produce melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color. While melanoma most commonly appears on the skin, it can also develop in the eyes and, in rare cases, in internal organs.
Unlike other skin cancers like basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma, melanoma is more likely to grow quickly and spread to other parts of the body. This makes early detection especially critical.
What Causes Melanoma?
The biggest risk factor for melanoma is ultraviolet (UV) radiation—primarily from sunlight and tanning beds. When UV rays damage the DNA in skin cells, it can lead to uncontrolled cell growth.
Other risk factors include:
- Fair skin, freckles, or light hair
- Family history of melanoma
- Having many moles, especially atypical ones
- A weakened immune system
- History of severe sunburns, especially during childhood
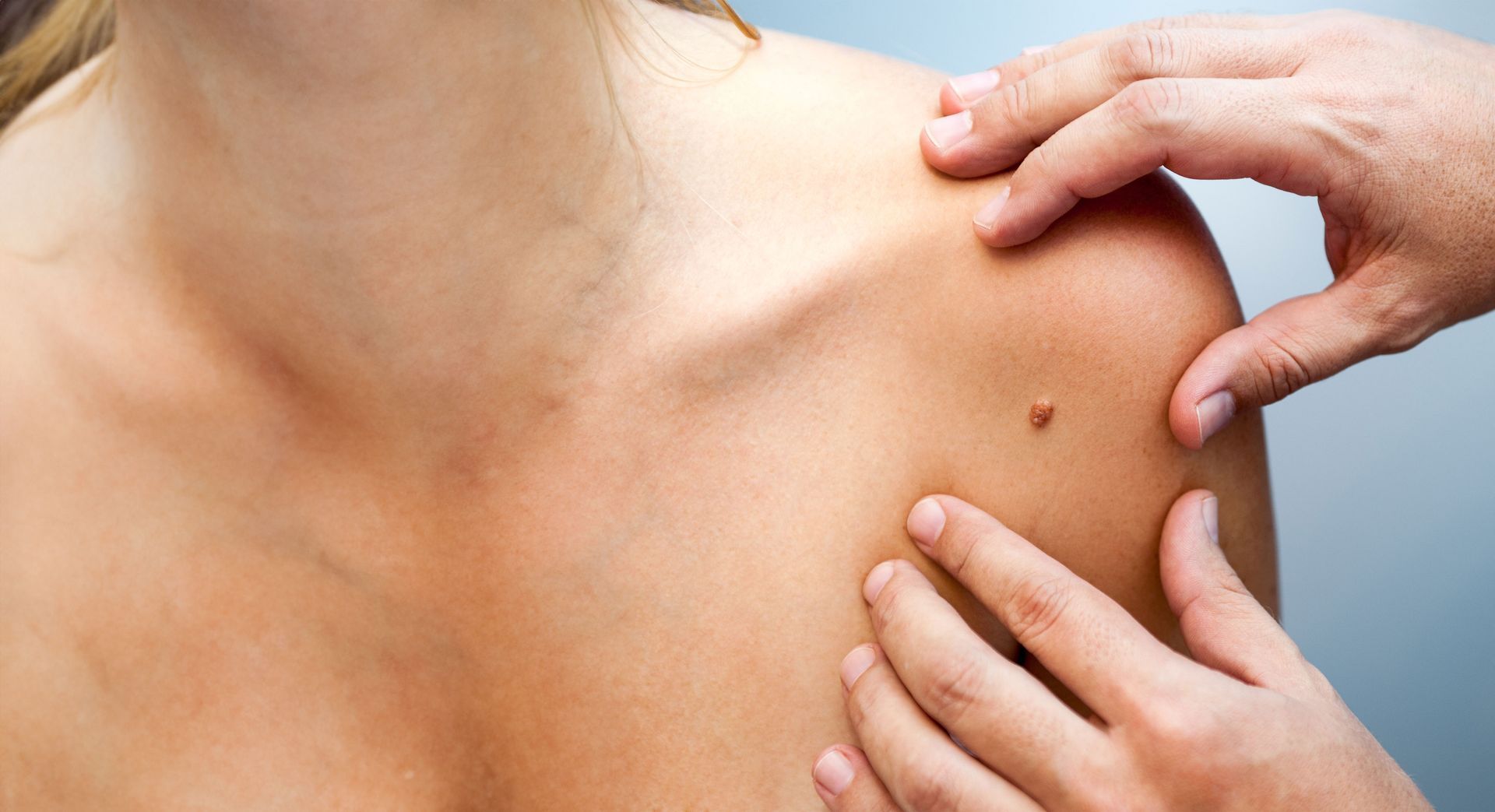
Signs and Symptoms: What to Look For
The best way to catch melanoma early is to monitor your skin regularly and know the signs. Dermatologists recommend using the ABCDE rule:
- Asymmetry: One half of the mole doesn’t match the other
- Border: Edges are irregular, ragged, or blurred
- Color: Uneven shades of black, brown, tan, or even red, white, or blue
- Diameter: Larger than 6 mm (about the size of a pencil eraser)
- Evolving: Any change in size, shape, color, or symptoms like itching or bleeding
If you notice any of these signs—or a new spot that just doesn’t look right—get it checked by a healthcare professional.
How Is Melanoma Diagnosed?
If your doctor suspects melanoma, they will likely perform a skin biopsy—removing part or all of the suspicious spot to examine it under a microscope. If melanoma is confirmed, further tests such as lymph node biopsies or imaging scans may be done to determine how far it has spread (called staging).
Melanoma Stages and Treatment
Melanoma is staged from 0 to IV:
- Stage 0–I: Localized and usually treatable with surgery alone.
- Stage II–III: May require additional treatments like immunotherapy, targeted therapy, or radiation.
- Stage IV: Advanced melanoma that has spread to distant organs. Treatment may involve systemic therapies such as immunotherapy or targeted drugs.
Thanks to advances in treatment—especially in immunotherapy—survival rates have improved significantly in recent years, even for advanced cases.
Can Melanoma Be Prevented To Sun Safety?
In many cases, yes. The key is sun safety:
- Wear broad-spectrum sunscreen (SPF 30 or higher)
- Avoid peak sun hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.)
- Wear protective clothing, sunglasses, and wide-brimmed hats
- Never use tanning beds
- Get regular skin checks, especially if you’re high-risk
The Bottom Line
Melanoma is serious, but it doesn’t have to be deadly. By staying informed, practicing sun safety, and catching suspicious spots early, you can significantly reduce your risk. Your skin is your body’s largest organ—take good care of it. Do a monthly self-skin check in front of a mirror. Don’t forget hidden areas like your scalp, the soles of your feet, and between your toes! Stay safe in the sun, and don’t skip those skin checks. Your future self will thank you. So, don't wait! Call Lumen Dermatology at 352-830-1500 and schedule your skin check today!